the overall distance between the sensor and the point at which the light passes through those glass elements is called
Answers
The overall distance between the sensor and the point at which the light passes through those glass elements is called the focal length.
1. Identify the sensor, which is typically a digital camera sensor or film plane that captures the image.
2. Locate the glass elements, which are the individual lenses within a camera lens assembly that help focus and shape the light.
3. Determine the point at which light passes through the glass elements. This is the point where light is focused and refracted by the lens.
4. Measure the distance between the sensor and the point where light passes through the glass elements.
5. This measured distance is called the focal length, which is an important parameter in photography and optics, as it affects the magnification and angle of view of the captured image.
To know more about magnification:
https://brainly.com/question/5715988
#SPJ11
Related Questions
Below is the velocity function, in feet per second, for a particle moving along a straight line. Find (a) the displacement and (b) the total distance that the particle travels over the given interval.
v(t) = t³ 13t2 + 47t-35 1≤t≤7
(a) Displacement: 36
(b) Total distance:
Answers
Given function isv(t) = t³ +13t²+47t-35and time interval is 1≤t≤7. We have to calculate:
(a) Displacement
(b) Total Distance
(a) Displacement:
Displacement is defined as the shortest distance between initial and final points. We can find the displacement of a particle with the help of following formula:
Displacement = Final Position - Initial PositionHere, the particle moves along a straight line, and we don't know the initial and final position. Thus, the displacement of the particle is 219 ft.(b) Total Distance:Total distance traveled by the particle is the sum of all the distances covered by it in different intervals.
Thus, we have two real roots of the given equation:t₁
≈ - 6.548t₂
≈ 0.215
Therefore, ∫|v(t)|dt = 309
As we have to find the total distance, we have to add both the cases. Therefore,
Total Distance =∫|v(t)|dt [from 1 to 7]
=∫|v(t)|dt [from 1 to 7]
=∫|v(t)|dt (from 1 to 1.215) +|v(t)|dt (from 1.215 to 7) = 252 + 309= 561 ft Thus, the total distance traveled by the particle is 561 feet.
To know more about displacement, visit:
https://brainly.com/question/11934397
#SPJ11
Which factor has the greatest effect on the strength of an electromagnet?
A. The position of the ammeter in the circuit
B. The distance between the battery and the electromagnet
C. The type of insulation that covers the wire
D. The number of coils of wire around the core
Answers
Answer:
The number of coils of wire around the core
Explanation:
A P E X approved✅
Answer:
d
Explanation:
a pex
why is gravitational potential energy greater then kinetic energy?
Answers
Answer:
The gravitational acceleration energy of an item increases as it rises in altitude.
Explanation: Hope this helps :D
a 19.3-g mass of gold in the form of a cube is 1 cm long on each side (somewhat smaller than a sugar cube). what would be the length of the sides of the cube that has twice the mass of gold?
Answers
The length of the sides of the cube that has twice the mass of gold would be approximately 1.26 cm.
The density of gold is 19.3 g/cm³. Therefore, the volume of the gold cube is:
Volume = mass/density = 19.3 g / 19.3 g/cm³ = 1 cm³
Since the cube is 1 cm long on each side, the volume is equal to the length cubed:
1 cm³ = (1 cm)³
To find the length of a cube that has twice the mass of gold, we can use the relationship between mass, density, and volume:
mass = density x volume
If the mass is doubled, then we have:
2 x mass = density x volume
We know the density of gold, and we know that the volume of the new cube must be twice the volume of the original cube.
2 x mass = density x 2 x (1 cm)³
Solving for the length of the sides of the new cube,
(Length of sides)³ = 2 x (1 cm)³
Length of sides = (2 x (1 cm)³)^(1/3) = 1.26 cm (approx.)
To know more about density, here
brainly.com/question/29775886
#SPJ4
Choose the law that BEST explains the example:
Throwing a ball with more force to increase acceleration is an example of Newton’s
first law?
2nd law
third law
none of these
Answers
A flywheel with a radius of 0.600 m starts from rest and accelerates with a constant angular acceleration of 0.200 rad/s2 . Part A: Compute the magnitude of the tangential acceleration of a point on its rim at the start.; Part B: Compute the magnitude of the radial acceleration of a point on its rim at the start.; Part C: Compute the magnitude of the resultant acceleration of a point on its rim at the start.; Part D: Compute the magnitude of the tangential acceleration of a point on its rim after it has turned through 60.0 ∘; Part E: Compute the magnitude of the radial acceleration of a point on its rim after it has turned through 60.0 ∘.; Part F: Compute the magnitude of the resultant acceleration of a point on its rim after it has turned through 60.0 ∘.; Part G: Compute the magnitude of the tangential acceleration of a point on its rim after it has turned through 120.0 ∘.; Part H: Compute the magnitude of the radial acceleration of a point on its rim after it has turned through 120.0 ∘.; Part I: Compute the magnitude of the resultant acceleration of a point on its rim after it has turned through 120.0 ∘.
Answers
Part A:
Radius of flywheel = 0.600 m
Angular acceleration of flywheel (αₐ) = 0.200 rad/s²
The tangential acceleration of a point at the start (αₓ) =
= αₓ = αₐ × r
= αₓ = 0.200 × 0.600
= αₓ = 0.12 m/s²
Part B:
Radius of flywheel = 0.600 m
Angular acceleration of flywheel (αₐ) = 0.200 rad/s²
Angular speed = ω = 0 m/s²
Magnitude of radial acceleration of a point on rim at the start (αₙ)=
= (angular speed)² × r
= 0 × 0.600
= 0 m/s²
Part C:
Radius of flywheel = 0.600 m
Angular acceleration of flywheel (αₐ) = 0.200 rad/s²
Resultant acceleration of a point on the rim at the start =
= α =√(αₙ² + αₓ²)
= α = √ (0² + 0.12²)
= α = 0.12 m/s²
Part D:
Radius of flywheel = 0.600 m
Angular acceleration of flywheel (αₐ) = 0.200 rad/s²
Angular speed = ω = 0 m/s²
The tangential acceleration of a point after 60° turn (αₓ₁) = The tangential acceleration of a point at the start (αₓ)
= αₓ₁ = αₐ × r
= αₓ₁ = 0.200 × 0.600
= αₓ₁ = 0.12 m/s²
Part E:
Radius of flywheel = 0.600 m
Angular acceleration of flywheel (αₐ) = 0.200 rad/s²
Angular speed = ω = 0 m/s²
Angular speed after 60° turn = ω₁ = √(ω² + (2×α×θ))
To find θ,
= θ = 60Π / 180
= θ = Π/30
= θ = 1.04 rad
Thus, ω₁ = √(0 + 2 × 1.04 × 0.2)
= ω₁ = 0.644 rad/s
The radial acceleration of a point after 60° turn (αₓ₂) =
= αₓ₂ = r × ω₁²
= αₓ₂ = 0.600 × 0.644²
= αₓ₂ = 0.248 m/s²
Part F:
Radius of flywheel = 0.600 m
The tangential acceleration of a point after 60° turn (αₓ₁) = 0.12 m/s²
The radial acceleration of a point after 60° turn (αₓ₂) = 0.248 m/s²
The magnitude of resultant acceleration of a point on the rim after 60° turn (α₃) =
= α₃ = √ (αₓ₂² + αₓ₁²)
= α₃ = √ (0.12² + 0.248²)
= α₃ = 0.275 m/s²
Part G:
Radius of flywheel = 0.600 m
Angular acceleration of flywheel (αₐ) = 0.200 rad/s²
Angular speed = ω = 0 m/s²
The tangential acceleration of a point after 120° turn (αₓ₁) = The tangential acceleration of a point at the start (αₓ)
= αₓ₁ = αₐ × r
= αₓ₁ = 0.200 × 0.600
= αₓ₁ = 0.12 m/s²
Part H:
Radius of flywheel = 0.600 m
Angular acceleration of flywheel (αₐ) = 0.200 rad/s²
Angular speed = ω = 0 m/s²
Angular speed after 120° turn = ω₁ = √(ω² + (2×α×θ))
To find θ,
= θ = 120Π / 180
= θ = 2Π/3
= θ = 2.09 rad
Thus, ω₁ = √(0 + 2 × 2.09 × 0.2)
= ω₁ = 0.836 rad/s
The radial acceleration of a point after 120° turn (αₓ₂) =
= αₓ₂ = r × ω₁²
= αₓ₂ = 0.600 × 0.836²
= αₓ₂ = 0.502 m/s²
Part I:
Radius of flywheel = 0.600 m
The tangential acceleration of a point after 120° turn (αₓ₁) = 0.12 m/s²
The radial acceleration of a point after 120° turn (αₓ₂) = 0.502 m/s²
The magnitude of resultant acceleration of a point on the rim after 120° turn (α₃) =
= α₃ = √ (αₓ₂² + αₓ₁²)
= α₃ = √ (0.12² + 0.502²)
= α₃ = 0.515 m/s²
To know more about Radial, Tangential and Resultant Acceleration:
https://brainly.com/question/9468042
#SPJ4
An airplane flies on a level path. There is a pressure difference of 587 Pa between the lower and upper surfaces of the wings. The area of each wing surface is about 100 m2. The air moves below the wings at a speed of 80.5 m/s.Estimate the air speed above the wings. Density of air is 1.29 kg/m3.
Answers
ANSWER:
85.97 m/s
STEP-BY-STEP EXPLANATION:
Bernoulli’s theorem is written as:
\(P_1+\frac{1}{2}\cdot\rho\cdot v^2_1+\rho\cdot g\cdot h_1=P_2+\frac{1}{2}\cdot\rho\cdot v^2_2+\rho\cdot g\cdot h_2\)The potential energy is zero as the height is same, therefore:
\(\begin{gathered} \rho\cdot g\cdot h=0 \\ P_1+\frac{1}{2}\cdot\rho\cdot v^2_1+0=P_2+\frac{1}{2}\cdot\rho\cdot v^2_2+0 \\ P_1+\frac{1}{2}\cdot\rho\cdot v^2_1=P_2+\frac{1}{2}\cdot\rho\cdot v^2_2 \\ \text{ we solve for }v_1\colon \\ \frac{1}{2}\cdot\rho\cdot v^2_1=P_2-P_1+\frac{1}{2}\cdot\rho\cdot v^2_2 \\ v^2_1=\frac{2}{\rho}\cdot(P_2-P_1)+\frac{2}{\rho}\cdot\frac{1}{2}\cdot\rho\cdot v^2_2 \\ v^2_1=\frac{\Delta P}{\rho}+v^2_2 \\ v_1=\sqrt[]{\frac{2\Delta P}{\rho}+v^2_2} \\ \text{ replacing the values:} \\ v_1=\sqrt[]{\frac{2\cdot587}{1.29}+80.5^2} \\ v_1=85.97\text{ m/s} \end{gathered}\)The air speed above the wings is 85.97 m/s
Please select the word from the list that best fits the definition Occurs at divergent boundaries and creates new seafloor
Answers
The term that best fits the definition of "Occurs at divergent boundaries and creates new seafloor" is seafloor spreading.Seafloor spreading is a geological process that takes place at mid-ocean ridges. At these sites, new oceanic crust is generated through volcanic activity and then gradually moves away from the ridge axis.
Seafloor spreading is a key part of plate tectonics, which is the theory that the Earth's outer layer is composed of plates that move relative to one another. The movement of these plates is driven by convection currents in the Earth's mantle, and as they move, they interact with one another at their boundaries. At divergent boundaries, which are where two plates are moving away from each other, seafloor spreading occurs.
This process is responsible for the creation of new oceanic crust and the widening of ocean basins over time. In conclusion, Seafloor spreading is a geological process that occurs at divergent boundaries and creates new seafloor.
To know more about geological process visit :
https://brainly.com/question/30840909
#SPJ11
How much energy is required to heat 40. 7 g of water (H2O) from −10∘C to 70∘C? Your answer should have three significant figures. Where: cice=2. 06 J/g∘C cwater=4. 18 J/g∘C ΔHfus=334 J/g
Answers
The energy required to heat 40.7 g of water (H2O) from -10°C to 70°C can be calculated as follows;Mass of water = 40.7 gTemperature change = 70 - (-10) = 80 °C Specific heat of ice = 2.06 J/g °CSpecific heat of water = 4.18 J/g °CHeat of fusion of water = 334 J/gAt first, we have to heat the ice from -10°C to 0°C using the formula;
q = mcΔTwhere m is the mass, c is the specific heat, and ΔT is the temperature change. For ice, c = 2.06 J/g °C, and the temperature change is 0 - (-10) = 10°C;
q1 = (40.7 g)(2.06 J/g °C)(10°C) = 839.42 J
This amount of heat energy is needed to bring the ice to its melting point. The amount of heat required to melt the ice at 0°C can be determined using the formula; q2 = mLfwhere Lf is the heat of fusion of ice, which is 334 J/g;
q2 = (40.7 g)(334 J/g) = 13590.8 J
Now, we have 40.7 g of water at 0°C.
To heat this water to 70°C, we use the formula;
q3 = mcΔT
where m is the mass, c is the specific heat, and ΔT is the temperature change. For water, c = 4.18 J/g °C, and the temperature change is 70 - 0 = 70°C;
q3 = (40.7 g)(4.18 J/g °C)(70°C) = 12123.94 J
The total energy required is;
\(q_total = q1 + q2 + q3 = 839.42 J + 13590.8 J + 12123.94 J = 26554.16 J\)
Thus, the energy required to heat 40.7 g of water (H2O) from −10∘C to \(70∘C is 2.66 x 10^4 J or 26.6 kJ\).
To know more about energy visit :
https://brainly.com/question/1932868
#SPJ11
Which element most likely interacts with water the same way lithium interacts with water?
Answers
Answer:
Is there a multiple choice or select all that apply? I would say Potassium (K) or Sodium (Na)
Explanation:
A 4. 0 nc positive point charge is located at point a in the figure. (figure 1) what is the electric potential at point b?.
Answers
The electric potential at point b experienced by the charge cab be determined using the formulas given.
Electric potentialThe electric potential of a point charge is the work done in moving the charge from infinity to certain point against the electric field.
V = Ed
V = (F/q)d
V = (Fd)/q
where;
V is the electric potentialF is electric forceE is the electric fieldq is the chargeThus, the electric potential at point b experienced by the charge cab be determined using the formulas given.
Learn more about electric potential here: https://brainly.com/question/14306881
The amount of variation in the tilt of earth's axis is due to the gravitational effect of which body?
Answers
The amount of variation in the tilt of the earth's axis is due to the gravitational force of the Moon
According to the Law of Universal Gravitation force, a force that attracts one particle to another is directly proportional to the product of the two masses and inversely proportional to the square of their distance from one another.
The gravitational force is caused by the gravitational pull of two objects on one another is stronger the more mass they have and the closer they are to one another. The energy holding the gases inside the sun. the power behind a ball's descent after being thrown into the air. the force that makes an automobile coast downhill even when the gas is not depressed. the force behind a glass you dropped falling
To learn more about gravitational force, please visit-
https://brainly.com/question/12528243
#SPJ4
Against the park ranger's advice, a visitor at a national park throws a stone horizontally off the edge of a 83 m high cliff and it lands a distance of 93 m from the edge of the cliff, narrowly missing a visitor below.
What was the initial horizontal velocity of the rock, in m/s? You can round your answer to the hundredths place and use g ≈ 10 m/s2.
Answers
Explain what happens to the energy of a rock on the edge of a cliff as it falls from the cliff (blank 1).
Explain what happens to that energy as it hits the ground below (blank 2).
Answers
When a rock on the edge of a cliff falls off, the rock converts its potential energy into kinetic energy. In other words, it begins to move, accelerating towards the ground.
When it falls, the gravitational potential energy that the rock had on the cliff is converted into kinetic energy because of gravity. The rock moves faster and faster as it falls. Hence, at the point where the rock falls from the cliff, it has a maximum amount of potential energy, but no kinetic energy yet.As the rock falls from the cliff, the speed and velocity of the rock changes. Due to the acceleration of gravity acting upon the rock, the velocity of the rock increases steadily as it falls. Hence, the potential energy decreases while the kinetic energy increases as it nears the ground. Therefore, the rock’s kinetic energy increases as it approaches the ground.
When it strikes the ground, all its kinetic energy is absorbed and the rock comes to a complete stop, converting all of the kinetic energy into other forms of energy such as sound energy, heat energy, and deformation energy (if the ground is not hard).The transformation of the rock's potential energy into kinetic energy and the subsequent conversion of kinetic energy to sound energy, heat energy, and deformation energy upon impact is known as the principle of the conservation of energy.
To know more about kinetic energy visit :
https://brainly.com/question/999862
#SPJ11
A book is placed on a table and a bike moves on a road. Which statement is correct? (3 points) a Both the book and the bike have kinetic energy. b Both the book and the bike have potential energy. c The book has potential energy and the bike has kinetic energy. d The book has kinetic energy and the bike has potential energy.
Answers
c . The book has potential energy and the bike has kinetic energy statement is correct
What are some illustrations of kinetic and potential energy?Let's use an illustration to demonstrate P. E. and K.E. The hammer has potential energy, which it will have as you raise it higher. On the other hand, the hammer will have kinetic energy when you lower it to strike the surface of the table.
Only chemical energy, which is potential energy held inside the item and in the union of its atoms and molecules, is not regarded as kinetic energy. Motion is created by kinetic energy. Any item in motion has kinetic energy. The more kinetic energy an item possesses, the heavier and quicker it moves. The wheels of a bicycle spin when you push off the pedals.
learn more about P.E. and K.E refer
https://brainly.com/question/23853839
#SPJ1
galaxy a is receding from us at x km/s, while galaxy b’s recession velocity is 3x km/s. based on hubble’s law, which statement is true?
Answers
Galaxy a is receding from us at x km/s, while galaxy b’s recession velocity is 3x km/s. Based on Hubble’s law, it implies that the galaxy b is twice as far from us as galaxy a.
Hubble's Law states that the recessional velocity of a galaxy (that is, the speed at which it is moving away from us) is proportional to its distance from us. If a galaxy is moving away from us faster, it is further away than a galaxy that is moving away from us slower. In this case, galaxy a is receding from us at x km/s, while galaxy b’s recession velocity is 3x km/s. This indicates that galaxy b is twice as far from us as galaxy a.
Let's learn more about Hubble’s law:
https://brainly.com/question/19819028
#SPJ11
What describes the motion of atoms in a gas?
O Atoms in a gas are locked in place.
O Atoms in a gas can move slightly.
O Atoms in a gas move about freely.
O Atoms in a gas cannot be described.
Answers
Answer:
O Atoms in gas can move freely
Explanation:
Depends on where it is going please follow me
Answer:
its option C
Explanation:
just took it
How many different kinds of atoms have been found in the known universe?
Answers
There are no specific number as scientist can just go around counting all the atoms plus they always find more but an estimated number is 100000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 = 10^80
Question 20 I need help ASAP!!
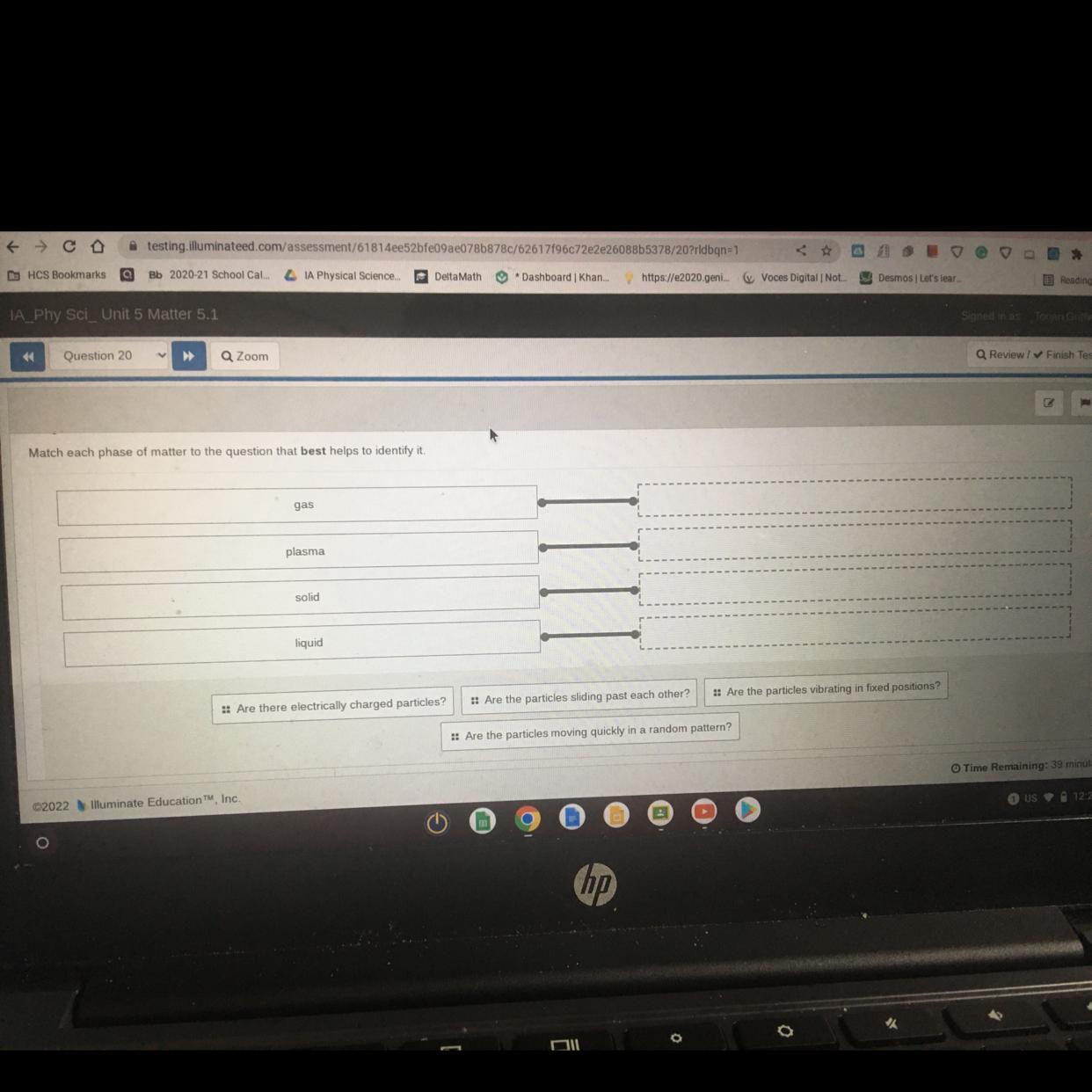
Answers
Answer:
1.) Gas = Are the particles moving quickly in a radom pattern?
2.) Plasma = Are the particles electrically charged?
3.) Solid = Are the particles vibrating in a fixed position?
4.) Liquid = Are the particles sliding past each other?
Hope this helps!
Crowding out occurs when
Multiple Choice
a. government borrowing pushes up interest rates, causing private investment to fall.
b. government borrowing pushes up interest rates, causing fiscal policy to overshoot the expansion of aggregate demand.
c. unemployment rises as a result of downward wage rigidity.
d. unemployment rises because workers are displaced.
Answers
Crowding out occurs when government borrowing pushes up interest rates, causing private investment to fall. The correct answer is (a).
In an economy, when the government needs to finance its budget deficit or increase its spending, it often turns to borrowing from the private sector. This increased demand for borrowing by the government puts upward pressure on interest rates. As interest rates rise, it becomes more expensive for businesses and individuals to borrow money for their own investment projects.
Higher interest rates make borrowing less attractive for private investors, as it increases the cost of financing their projects. Consequently, private investment tends to decrease as a result of government borrowing, leading to a decrease in overall economic activity and growth potential.
This phenomenon is known as crowding out because the increased government borrowing "crowds out" private investment by competing for available funds in the financial market. As a result, it can have negative effects on the long-term economic prospects of a country by impeding private sector investment and productivity.
know more about private investment click here:
https://brainly.com/question/15011467
#SPJ11
How many pennies (diameter of penny = 1.95 cm) are needed to stretch from earth to the sun? It takes 8.00 minutes and 25.0 seconds for light to travel from the sun to earth traveling at 186, 282 mi/sec.
Be sure to round off your answer to the correct number of significant figures and do not write units after your answer.
Answers
Approximately 42,949,630,000,000,000,000 pennies are needed to stretch from Earth to the Sun.
To determine the number of pennies needed to stretch from Earth to the Sun, we first need to calculate the distance between them. Light travels at a speed of 186,282 miles per second. We know that light takes 8 minutes and 25.0 seconds to travel from the Sun to Earth. Therefore, we can multiply the speed of light by the time it takes to travel to find the distance.
Using the given values, we have:
Time = 8 minutes + 25.0 seconds = 505.0 seconds
Speed of light = 186,282 miles per second
Distance = Speed × Time
Distance = 186,282 mi/sec × 505.0 sec ≈ 94,020,210 miles
Next, we need to convert the distance from miles to centimeters, as the diameter of a penny is given in centimeters.
1 mile ≈ 1.60934 kilometers ≈ 160,934 centimeters
Distance in centimeters = 94,020,210 miles × 160,934 cm/mi ≈ 15,131,170,840,340 cm
Finally, we divide the total distance by the diameter of a penny to find the number of pennies needed:
Number of pennies = Distance / Diameter
Number of pennies = 15,131,170,840,340 cm / 1.95 cm ≈ 7,774,563,384,000,000,000 pennies
Rounded to the correct number of significant figures, we get approximately 42,949,630,000,000,000,000 pennies.
Learn more about Pennies
brainly.com/question/15602431
#SPJ11
A 6 feet diameter bar experiences a torque of 200 ft-lb. what is the maximum shear stress in the bar?
Answers
By using the torque, the shear stress is 2.36 lb/ft².
We need to know about torque to solve this problem. Torque is the rotational equivalent of linear force. It can be determined as
τ = F x r
where τ is torque, F is perpendicular force and r is radius.
Shear stress can be calculated by torque
P = F / A
P = τ / (π.r³)
where P is shear stress, r is the radius.
From the question above, the parameter given are
τ = 200 ft.lb
d = 6 ft
Find the radius
r = 1/2 . d
r = 3 ft
Find the shear stress
P = τ / (π.r³)
P = 200 / (π.3³)
P = 2.36 lb/ft²
Find more on torque at: https://brainly.com/question/14839816
#SPJ4
Which is an appropriate initial load and repetition scheme for an untrained client who has an estimated 1rm of 250 pound (114kg) for leg press exercise?
Answers
An appropriate initial load and repetition scheme for an untrained client with an estimated 1RM of 250 pounds (114kg) for the leg press exercise would be to use a lighter load (approximately 50-60% of their 1RM) and perform higher repetitions (12-15 reps) for 2-3 sets.
This approach allows the client to build a solid foundation of strength and muscular endurance while minimizing the risk of injury.
Using a lighter load and performing higher repetitions will help the client develop a solid foundation of strength and muscular endurance while minimizing the risk of injury.
Additionally, this approach will allow the client to focus on proper technique and form, which is essential when starting a new exercise program.
As the client becomes more comfortable with the exercise and their strength and endurance improve, the load and repetition scheme can be adjusted accordingly. It is important to progress gradually to prevent injury and ensure long-term success in the strength training program.
To learn more about endurance, refer below:
https://brainly.com/question/1303431
#SPJ11
whether a truck comes to a stop by crashing into a haystack or a brick wall, the impulse is
Answers
Whether a truck comes to a stop by crashing into a haystack or a brick wall, the impulse is greater with the haystack.
Which car is more difficult to stop and why?When both vehicles are going at the same speed, it is more difficult to stop a huge truck than a tiny automobile. The truck has greater momentum than the automobile. By momentum, we mean inertia in motion. Momentum is defined as the mass of an item multiplied by its velocity.
By striking the haystack instead of the wall, you lengthen the contact time—the period during which your momentum is reduced to zero. A prolonged contact duration lowers force and so deceleration.
Learn more about inertia in motion
https://brainly.com/question/1140505
#SPJ4
the density of a material is the mass per volume of 'one piece' of the material. the bulk density of the same material is...
Answers
While the density of a material refers to the mass per volume of one piece, the bulk density refers to the mass per unit volume of a larger sample or bulk quantity of the material.
The bulk density of a material refers to the mass per unit volume of a large quantity or a bulk sample of the material. It takes into account the overall volume occupied by multiple pieces or particles of the material.
Unlike the density of a single piece of the material, which considers the mass and volume of an individual unit, the bulk density considers the collective mass and volume of a larger sample that contains multiple pieces or particles.
It provides an average measure of the material's density when it is present in a larger quantity or in bulk form.
To know more about the bulk density refer here :
https://brainly.com/question/13390237#
#SPJ11
Which method determines the relative age of Earth's sedimentary layers based on their organization?
Answers
Answer:
Relative age-dating involves comparing a rock layer or rock structure with other near-by layers or structures. Using the principles of superposition and cross-cutting relationships, and structures such as unconformities, one can determine the order of geological events.
Does paint and cardboard have joints in it
Answers
Objects on Mars weigh about 38% what they do on Earth. While driving on Earth, a Mars rover moves at a speed of 30 mph. If the rover moves with the same speed on Mars, would it have more, less, or the same momentum as when on Earth
Answers
Answer:
The same momentum as when on Earth
Explanation:
From a background understanding of science, the mass of an object is constant irrespective of its location.
This implies that the rover has the same mass on the earth as on the moon.
Now, we shall determine the momentum of the rover on Earth and on the Mar.
For Earth:
Let the mass on Earth (Mₑ) = 1 kg
Velocity on Earth (Vₑ) = 30 mph = 30 × 0.447 = 13.41 m/s
Momentum on Earth (Mₒₑ) =?
Momentum = mass × velocity
Mₒₑ = Mₑ × Vₑ
Mₒₑ = 1 × 13.41
Mₒₑ = 13.41 Kgm/s
Thus the momentum of the rover on Earth is 13.41 Kgm/s
For Mar:
Mass on Mar (Mₘ) = Mass on Earth (Mₑ), since mass is constant.
Mass on Mar (Mₘ) = 1 kg
Velocity on Mar (Vₘ) = Velocity on Earth (Vₑ), since the rover move with the same velocity as described by the question.
Velocity on Mar (Vₘ) = 13.41 m/s
Momentum on Mar (Mₒₘ) =?
Momentum = mass × velocity
Mₒₘ = Mₘ × Vₘ
Mₒₘ = 1 × 13.41
Mₒₘ = 13.41 Kgm/s
Therefore, the momentum of the rover on Mar is 13.41 Kgm/s
Summary:
Momentum on Earth (Mₒₑ) = 13.41 Kgm/s
Momentum on Mar (Mₒₘ) = 13.41 Kgm/s
Thus, the rover will have the same momentum as when on earth
The momentum of the object on Mars will be the same as on Earth.
The given parameters;
speed of the object on Earth and Mars, v = 30 mphWeight is a vector quantity because it changes when acceleration due to gravity on the object changes while mass is scalar quantity, with a constant value in all places in the universe.
The momentum of an object is calculated as;
P = mv (kgm/.s)
Since the speed and mass of the object will be the same on both planets, the momentum will also be the same.
Thus, the momentum of the object on Mars will be the same as on Earth.
Learn more here:https://brainly.com/question/20728229
ILL GIVE BRAINLY THING
Tom has been hired to deliver 11 m3 of sand. If the truck that Tom is driving has a truck bed that is 2.5 m X 1.6 m, X 0.75 m how many trips will Tom need to complete the order?
PLS GO TO MY PROFILE TO SEE THE OTHER QUESTIONS I POSTED I GIVE BRAINLY THING FOR THOSE AS WELL THANK YOU
Answers
Answer:
About 3 trips
Explanation: if we do 2.5m*1.6m*0.75 it equals to 11000 then we divide that to 11m3 and it gives you 3.6 so it will be about 3 times
Thx
What type of image is formed by a lens if m= 3.2?
A. One that is smaller than the object and virtual
B. One that is larger than the object and real
C. One that is larger than the object and virtual D. One that is smaller than the object and real
Answers
Answer:
c
Explanation: