Answers
Answer:98
Explanation:hope this helps!
Related Questions
An insulating vessel contains 80 g of a block of ice at -12 °C. If 450 g of water at 60 °C is added to the ice in the vessel: (i) (ii) AM Determine whether or not the ice will melt completely; Calculate the final temperature of the system. [ specific heat capacity of ice = 2100 J kg ¹K-¹, latent heat of fusion of ice = 3.33 x 10³ J K-¹, specific heat capacity of water = 4200 J kg ¹K-¹] [6 marks] and hy convection.
Answers
An insulating vessel contains 80 g of a block of ice at -12 °C. If 450 g of water at 60 °C is added to the ice in the vessel, Energy required for complete melting = \(80 g X (3.33 X 10^3 J/kg)\).
To determine whether the ice will soften absolutely and calculate the final temperature of the system, we need to do not forget the strength transferred among the ice and water at some stage in the procedure.
(i) To decide if the ice will melt completely, we need to examine the energy won by using the ice to the electricity required for complete melting.
Energy received by way of the ice = mass of ice × particular heat capacity of ice × alternate in temperature
Energy won by using the ice = eighty g × 2100 J/(kg·°C) × (final temperature - (-12°C))
Energy required for complete melting = mass of ice × latent warmth of fusion of ice
Energy required for whole melting = 80 g × (3.33 × 10^3 J/kg)
If the strength received via the ice is extra than or same to the electricity required for entire melting, the ice will soften completely.
(ii) To calculate the very last temperature of the gadget, we want to keep in mind the power transferred between the ice and water.
Energy won by the water = mass of water × unique heat ability of water × trade in temperature
Energy received by using the water = 450 g × 4200 J/(kg·°C) × (final temperature - 60°C)
Since electricity is conserved inside the machine, the power gained by means of the ice and water need to be identical:
Energy gained through the ice = Energy won by the water
Using the equations above, we will installation the following equation:
80 g × 2100 J/(kg·°C) × (very last temperature - (-12°C)) = 450 g × 4200 J/(kg·°C) × (very last temperature - 60°C)
Thus, this the final temperature of the system.
For more details regarding temperature, visit:
https://brainly.com/question/7510619
#SPJ1
The diagram below shows the velocity vectors for two cars that are moving
relative to each other.
45 m/s west
25 m/s east
Car 1
Car 2
From the frame of reference of car 1, what is the velocity of car 2?
OA. 20 m/s west
OB. 70 m/s east
C. 70 m/s west
D. 20 m/s east
Answers
The relative velocity of the car 2 with respect to car 1 is 70 m/s west. So, the correct option is C.
Velocity of the car 1 with respect to the ground, v₁ = 45 m/s west
Velocity of the car 2 with respect to the ground, v₂ = 25 m/s east
Let the direction towards the east be positive and the opposite direction towards the west be negative.
The expression for the relative velocity of the car 2 with respect to car 1 is given by,
v₂₁ = v₂ - v₁
v₂₁ = 25 - (-45)
Therefore, the relative velocity,
v₂₁ = 70 m/s west
To learn more about relative velocity, click:
https://brainly.com/question/29655726
#SPJ1
Attaching the image file here.

Two tuning forks with frequencies of 256 Hz and 512 Hz are struck. Which of the sounds will move faster through the air?
Answers
Answer:
Two tuning forks with frequencies of 256 Hz and 512 Hz are struck. Which of the sounds will move faster through the air? Neither, the speed of sound is constant in air.
A metal wire of length 1cm and of uniform diameter has a resistance of 0.8 ohms. What is the resistance of a 50cm wire coil made of the same material but having twice its diameter?
Answers
Answer:
20
Explanation:
R= resistance P = resistivity
L = length A = area
0.8 = 1cm/A
R = J l/A => 0.8* 50*A/A
=> 0.8 * 25
=> 20
Answer:
Resistance is directly proportional to length, inversely proportional to cross-sectional area. Pay attention in class, and observe that even easy multiple choice questions can have only wrong answers if the setter makes a mistake.
An object of mass 2kg moves in circles at radius 8m at uniform speed of 30m/s calculate. A_angular velocity B_ceritripetal force
Answers
The angular velocity is 3.75 m/s and the centripetal force is 225 N respectively.
The angular velocity of an object with respect to some extent is a degree of the way rapid that item actions through the point's view, within the feel of the way speedy the angular function of the item modifications. An instance of angular pace is a ceiling fan. One blade will whole a complete round in a certain amount of time T, so its angular speed with respect to the middle of the ceiling fan is twoπ/T.
Calculation:-
A. angular velocity ω = v/r
= 30 /8
= 3.75 m/s
B. Centripetal force = mv²/r
= 2×30²/8
= 225 N
There are 3 formulations we will use to find the angular velocity. the primary comes instantly from the definition. The angular pace is the rate of alternate of the position attitude of an object with respect to time, so w = theta / t, in which w = angular pace, theta = position attitude, and t = time.
Learn more about angular velocity here:-brainly.com/question/20432894
#SPJ9
A car starts from rest and accelerates at a constant rate in a straight line. In the first second the car moves a distance of 2.0 meters. How much additional distance will the car move during the second second of its motion?
Answers
Since the car is accelerating at a constant rate, the distance it travels during each second of its motion will be directly proportional to the time it has been accelerating.
In the first second, the car moved a distance of 2 meters, and in the second second, it will move twice the distance of the first second, so the car will move additional distance of 2*2 = 4 meters during the second second of its motion.
The distance traveled during the second second of its motion is 1/2 * 2 = 1 meters.
A car that accelerates at a constant rate will move a distance equal to the initial velocity multiplied by time plus 1/2 the acceleration multiplied by the square of time. Since the car starts from rest, the initial velocity is zero.
Therefore, the distance traveled during the second second is 1/2 * acceleration \(* (time)^2 = 1/2 * a * t^2 = 1/2 * a * 1^2 = 1/2 * a\) Since the car moved 2.0 meters in the first second, it means the acceleration is\(2m/s^2\), and the distance traveled during the second second is 1/2 * 2 = 1 meters.
Learn more about initial velocity:
https://brainly.com/question/9365999
What would the world be like without right triangles? How are they used to calculate every item (what measurements are used? Give an example of how you would calculate an item or side of a right triangle.
Answers
The concept of right triangles is applied in different areas in real life. The areas include survey, carpentry, calculations involving ladder heights, etc. The are used by applying the pythagorean theorem which is expressed as
hypotenuse^2 = opposite side^2 + adjacent side^2
where hypotenuse is the longest side of the triangle and the opposite and adjacent sides are the legs of the triangle.
An example is the position of a ladder leaning on a wall. The angle that the ladder would make with the ground, the required length of the ladder and the distance from the wall can be calculated.
If we want to calculate the length of a ladder required to reach a certain height on a buliding, the length of the reuired ladder would be the hypotenuse of the right triangle formed. the height to be accessed would be the opposite side of the triangle. The distance between the foot of the ladder and the building would be the adjacent side of the triangle.
Question 3 (5 points)
Match the images with the correct fossil type,
А
B
C
D
E
Answers
Answer:
There no image
Explanation:
Question 3
By what volume would 25 L of alcohol increase if its temperature was
increased from 20°C to 30°C? (3 marks)
Answers
Answer:
V2 = 37.5 L
Explanation:
Given the following data;
Initial volume, V1 = 25 L
Initial temperature, T1 = 20°C
Final temperature,T2 = 30°C
To find the final volume V2, we would use Charles' law;
Charles states that when the pressure of an ideal gas is kept constant, the volume of the gas is directly proportional to the absolute temperature of the gas.
Mathematically, Charles is given by;
\( \frac {V}{T} = K\)
\( \frac{V_{1}}{T_{1}} = \frac{V_{2}}{T_{2}} \)
Making V2 as the subject formula, we have;
\( V_{2}= \frac{V_{1}}{T_{1}} * T_{2}\)
\( V_{2}= \frac{25}{20} * 30 \)
\( V_{2}= 1.25 * 30 \)
V2 = 37.5 L
See Conceptual Example 6 to review the concepts involved in this problem. A 12.0-kg monkey is hanging by one arm from a branch and swinging on a vertical circle. As an approximation, assume a radial distance of 86.4 cm is between the branch and the point where the monkey's mass is located. As the monkey swings through the lowest point on the circle, it has a speed of 1.33 m/s. Find (a) the magnitude of the centripetal force acting on the monkey and (b) the magnitude of the tension in the monkey's arm.
Answers
Answer:
(a) 24.56 N
(b) 142.28 N
Explanation:
(a)
The designation assigned to something like the net force pointed toward the middle including its circular route seems to be the centripetal force. The net stress only at lowest point constitutes of the strain throughout the arm projecting upward towards the middle as well as the weight pointed downwards either backwards from the center.
The centripetal function is generated from either scenario by Equation:
⇒ \(Fc = \frac{mv^2}{r}\)
On putting the values, we get
⇒ \(=\frac{12\times 1.33^2}{0.864}\)
⇒ \(=24.56 \ N\)
(b)
Use T to denote whatever arm stress we can get at the bottom including its circle:
⇒ \(Fc = T - mg =\frac{ mv^2}{r}\)
⇒ \(T = mg + Fc\)
⇒ \(=12\times 9.81+24.56\)
⇒ \(=142.28 \ N\)
Which observation is evidence that electromagnetic radiation (EMR) has particle-like
properties? (1 point)
O EMR refracts as it moves into a different medium.
O
A diffraction pattern is observed when EMR passes through a narrow slit.
O Some EMR is blocked when it passes through a polarized lens.
O EMR with energy above a certain value can eject electrons out of a metal.
Answers
The observation that electromagnetic radiation with energy above a certain value can eject electrons out of a metal is a piece of evidence that they have particle-like properties.
Electromagnetic radiations as particlesThe observation that electromagnetic radiation with energy above a certain value can eject electrons out of a metal is a piece of evidence that they have particle-like properties.
This observation that electromagnetic radiation behaves like particles is known as the photoelectric effect.
It provides evidence that electromagnetic radiation exhibits particle-like properties. When EMR with sufficient energy (above a certain threshold) interacts with a metal surface, it can cause the ejection of electrons from the metal.
This behavior indicates that EMR behaves as discrete packets of energy called photons, which transfer their energy to the electrons and cause their release. The photoelectric effect supports the particle nature of EMR and is a fundamental concept in the field of quantum mechanics.
More on electromagnetic radiation can be found here: https://brainly.com/question/29646884
#SPJ1
A small lead ball, attached to a 1.10-m rope, is being whirled in a circle that lies in the vertical plane. The ball is whirled at a constant rate of three revolutions per second and is released on the upward part of the circular motion when it is 1.3 m above the ground. The ball travels straight upward. In the absence of air resistance, to what maximum height above the ground does the ball rise
Answers
Answer:
1.84 m
Explanation:
For the small lead ball to be balanced at the tip of the vertical circle just before it is released, the reaction force , N equal the weight of the lead ball W + the centripetal force, F. This normal reaction ,N also equals the tension T in the string.
So, T = mg + mrω² = ma where m = mass of small lead ball, g = acceleration due to gravity = 9.8 m/s², r = length of rope = 1.10 m and ω = angular speed of lead ball = 3 rev/s = 3 × 2π rad/s = 6π rad/s = 18.85 rad/s and a = acceleration of normal force. So,
a = g + rω²
= 9.8 m/s² + 1.10 m × (18.85 rad/s)²
= 9.8 m/s² + 390.85 m/s²
= 400.65 m/s²
Now, using v² = u² + 2a(h₂ - h₁) where u = initial velocity of ball = rω = 1.10 m × 18.85 rad/s = 20.74 m/s, v = final velocity of ball at maximum height = 0 m/s (since the ball is stationary at maximum height), a = acceleration of small lead ball = -400.65 m/s² (negative since it is in the downward direction of the tension), h₁ = initial position of lead ball above the ground = 1.3 m and h₂ = final position of lead ball above the ground = unknown.
v² = u² + 2a(h₂ - h₁)
So, v² - u² = 2a(h₂ - h₁)
h₂ - h₁ = (v² - u²)/2a
h₂ = h₁ + (v² - u²)/2a
substituting the values of the variables into the equation, we have
h₂ = 1.3 m + ((0 m/s)² - (20.74 m/s)²)/2(-400.65 m/s²)
h₂ = 1.3 m + [-430.15 (m/s)²]/-801.3 m/s²
h₂ = 1.3 m + 0.54 m
h₂ = 1.84 m
two cars A and B are 600 meters apart car A travels due east at some speed per on a collision course with car b which travels due west at half speed as car A if the two cars fatally collide with each other in 5 seconds how fast was car A going?
Answers
Answer:
Car A was going at 80 m/s
Explanation:
Let's call "x" the unknown speed of car A. In such case, the speed of car B would be x/2.
We proceed to describe the distance covered by car A (dA) in the 5 seconds it took to collide: dA = speed * time = x * 5 = 5 x
Now the distance covered by car B (dB) in the same time would be:
dB = speed * time = (x/2) * 5 = 5 x / 2
Now, we know that the distance that separated both cars was 600 meters, so the addition of what car A covered plus what car B covered must equal 600 m, and in equation form:
dA + dB = 600
5 x + 5 x / 2 = 600
combining like terms:
15 x / 2 = 600
multiplying both sides by 2:
15 x = 1200
divide both sides by 15:
x = 80 m/s
This is the speed of car A.
The proper mean lifetime of a muon is 2.2 × 10–6 s. A beam of muons is moving with speed 0.6c relative to an inertial observer. Approximately how far will a muon in the beam travel, on average, before it decays?
Answers

The distance travelled by the muon is 316.8 meter, before it decays.
What is proper mean lifetime?In radioactivity, mean life refers to the cumulative lifetime of all the nuclei of a specific unstable atomic species. This period of time can be conceptualised as the product of the lifespan of each individual unstable nucleus in a sample divided by the overall number of unstable nuclei present. A specific species of unstable nucleus's half-life is always 1.443 times shorter than its mean life.
The proper mean lifetime of a muon is 2.2 × 10⁻⁶ s.
Speed of the muon is 0.6c.
Hence, the distance travelled by the muon is = 0.6c × 2.2 × 10⁻⁶ s.
= 0.6 × 3 × 10⁸×2.2 × 10⁻⁶ meter
= 396 meter.
In relativistic observation, the distance travelled by the muon is = 396 ×√(1 - (0.6c/c)²) meter
= 316.8 meter
Learn more about mean lifetime here:
https://brainly.com/question/29390781
#SPJ2
Can someone explain how to do the algebra for this question? I know everything else, I just don’t know how to rearrange the question to solve for v.

Answers
Answer:
Refer to the step-by-step Explanation.
Step-by-step Explanation:
Simplify the equation with given substitutions,
Given Equation:
\(mgh+(1/2)mv^2+(1/2)I \omega^2=(1/2)mv_{_{0}}^2+(1/2)I \omega_{_{0}}^2\)
Given Substitutions:
\(\omega=v/R\\\\ \omega_{_{0}}=v_{_{0}}/R\\\\\ I=(2/5)mR^2\)\(\hrulefill\)
Start by substituting in the appropriate values: \(mgh+(1/2)mv^2+(1/2)I \omega^2=(1/2)mv_{_{0}}^2+(1/2)I \omega_{_{0}}^2 \\\\\\\\\Longrightarrow mgh+(1/2)mv^2+(1/2)\bold{[(2/5)mR^2]} \bold{[v/R]}^2=(1/2)mv_{_{0}}^2+(1/2)\bold{[(2/5)mR^2]}\bold{[v_{_{0}}/R]}^2\)
Adjusting the equation so it easier to work with.\(\Longrightarrow mgh+\dfrac{1}{2} mv^2+\dfrac{1}{2} \Big[\dfrac{2}{5} mR^2\Big]\Big[\dfrac{v}{R} \Big]^2=\dfrac12mv_{_{0}}^2+\dfrac12\Big[\dfrac25mR^2\Big]\Big[\dfrac{v_{_{0}}}{R}\Big]^2\)
\(\hrulefill\)
Simplifying the left-hand side of the equation:
\(mgh+\dfrac{1}{2} mv^2+\dfrac{1}{2} \Big[\dfrac{2}{5} mR^2\Big]\Big[\dfrac{v}{R} \Big]^2\)
Simplifying the third term.
\(\Longrightarrow mgh+\dfrac{1}{2} mv^2+\dfrac{1}{2} \Big[\dfrac{2}{5} mR^2\Big]\Big[\dfrac{v}{R} \Big]^2\\\\\\\\\Longrightarrow mgh+\dfrac{1}{2} mv^2+\dfrac{1}{2}\cdot \dfrac{2}{5} \Big[mR^2\Big]\Big[\dfrac{v}{R} \Big]^2\\\\\\\\\Longrightarrow mgh+\dfrac{1}{2} mv^2+\dfrac{1}{5} \Big[mR^2\Big]\Big[\dfrac{v}{R} \Big]^2\)
\(\\ \boxed{\left\begin{array}{ccc}\text{\Underline{Power of a Fraction Rule:}}\\\\\Big(\dfrac{a}{b}\Big)^2=\dfrac{a^2}{b^2} \end{array}\right }\)
\(\Longrightarrow mgh+\dfrac{1}{2} mv^2+\dfrac{1}{5} \Big[mR^2\Big]\Big[\dfrac{v^2}{R^2} \Big]\\\\\\\\\Longrightarrow mgh+\dfrac{1}{2} mv^2+\dfrac{1}{5} \Big[mR^2 \cdot\dfrac{v^2}{R^2} \Big]\)
"R²'s" cancel, we are left with:
\(\Longrightarrow mgh+\dfrac{1}{2} mv^2+\dfrac{1}{5} \Big[mR^2\Big]\Big[\dfrac{v^2}{R^2} \Big]\\\\\\\\\Longrightarrow mgh+\dfrac{1}{2} mv^2+\dfrac{1}{5}mv^2\)
We have like terms, combine them.
\(\Longrightarrow mgh+\dfrac{1}{2} mv^2+\dfrac{1}{5} \Big[mR^2\Big]\Big[\dfrac{v^2}{R^2} \Big]\\\\\\\\\Longrightarrow mgh+\dfrac{7}{10} mv^2\)
Each term has an "m" in common, factor it out.
\(\Longrightarrow m(gh+\dfrac{7}{10}v^2)\)
Now we have the following equation:
\(\Longrightarrow m(gh+\dfrac{7}{10}v^2)=\dfrac12mv_{_{0}}^2+\dfrac12\Big[\dfrac25mR^2\Big]\Big[\dfrac{v_{_{0}}}{R}\Big]^2\)
\(\hrulefill\)
Simplifying the right-hand side of the equation:
\(\Longrightarrow \dfrac12mv_{_{0}}^2+\dfrac12\cdot\dfrac25\Big[mR^2\Big]\Big[\dfrac{v_{_{0}}}{R}\Big]^2\\\\\\\\\Longrightarrow \dfrac12mv_{_{0}}^2+\dfrac15\Big[mR^2\Big]\Big[\dfrac{v_{_{0}}}{R}\Big]^2\\\\\\\\\Longrightarrow \dfrac12mv_{_{0}}^2+\dfrac15\Big[mR^2\Big]\Big[\dfrac{v_{_{0}}^2}{R^2}\Big]\\\\\\\\\Longrightarrow \dfrac12mv_{_{0}}^2+\dfrac15\Big[mR^2\cdot\dfrac{v_{_{0}}^2}{R^2}\Big]\\\\\\\\\Longrightarrow \dfrac12mv_{_{0}}^2+\dfrac15mv_{_{0}}^2\Big\\\\\\\\\)
\(\Longrightarrow \dfrac{7}{10}mv_{_{0}}^2\)
Now we have the equation:
\(\Longrightarrow m(gh+\dfrac{7}{10}v^2)=\dfrac{7}{10}mv_{_{0}}^2\)
\(\hrulefill\)
Now solving the equation for the variable "v":
\(m(gh+\dfrac{7}{10}v^2)=\dfrac{7}{10}mv_{_{0}}^2\)
Dividing each side by "m," this will cancel the "m" variable on each side.
\(\Longrightarrow gh+\dfrac{7}{10}v^2=\dfrac{7}{10}v_{_{0}}^2\)
Subtract the term "gh" from either side of the equation.
\(\Longrightarrow \dfrac{7}{10}v^2=\dfrac{7}{10}v_{_{0}}^2-gh\)
Multiply each side of the equation by "10/7."
\(\Longrightarrow v^2=\dfrac{10}{7}\cdot\dfrac{7}{10}v_{_{0}}^2-\dfrac{10}{7}gh\\\\\\\\\Longrightarrow v^2=v_{_{0}}^2-\dfrac{10}{7}gh\)
Now squaring both sides.
\(\Longrightarrow \boxed{\boxed{v=\sqrt{v_{_{0}}^2-\dfrac{10}{7}gh}}}\)
Thus, the simplified equation above matches the simplified equation that was given.
The diagram below shows four layers of Earth.
The picture shows the internal structure of Earth. The central region is labeled 'A.' The layer around the central region is labeled 'B.' The outermost layer is labeled 'D.' The layer inside Earth which is just after layer D is labeled 'C.'
In which of these layers does hot material move upwards and cool material sink downwards?
Layer A
Layer B
Layer C
Layer D
Answers
Answer:
Layer C
Explanation:
Hope this helps!
-Liyah<3
Directions: One of the biggest myths in weight management is that a short-term fad diet will help you lose weight and keep it off. Below is a list of current fad diets. Read the short description of each, and answer the questions based on your knowledge of healthy eating.


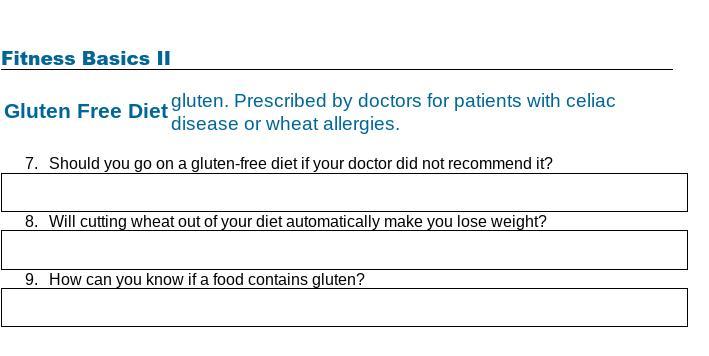

Answers
1. Completely cutting out food groups, such as grains, fruits, and vegetables, can have negative health implications as each food group provides essential nutrients.
2. Is this eating a sustainable oneThis eating pattern of high meat and protein intake while restricting grains, fruits, and vegetables may not be sustainable over a lifetime, as it lacks balance and variety.
3. Three healthy foods that would be restricted in this diet are grains, fruits, and vegetables. These foods are important as they provide essential nutrients, antioxidants, and dietary fiber, supporting overall health, digestion, and reducing the risk of chronic diseases. Restricting these foods can lead to nutrient deficiencies and negatively impact well-being.
Read more on healthy foods here:https://brainly.com/question/30784972
#SPJ1
b. Density and relative density.

Answers
Explanation:
density, mass of a unit volume of a material substance. The formula for density is d = M/V, where d is density, M is mass, and V is volume. Density is commonly expressed in units of grams per cubic centimetre.
The relative density of a substance is defined as the ratio of the density of that substance to the density of water at 4oC. It is also defined as the ratio of the mass of substance to the mass of equal volume of water at 4oC. i.e., R.D. = Mass of the substance / mass of an equal volume of water at 4oC
A roller coaster is at a peak of 20m and has a mass of 900kg. What is the potential energy of the roller coaster?
O 100000 J
10000 J
O 9.8 J
O 176400 J
Answers
The potential energy of the roller coaster is 176,400 J (joules).
The potential energy of an object is given by the formula PE = mgh, where PE is the potential energy, m is the mass of the object, g is the acceleration due to gravity, and h is the height or vertical position of the object.
In this case, the roller coaster is at a peak of 20m and has a mass of 900kg. The acceleration due to gravity, g, is approximately 9.8 \(m/s^2\).
Using the formula, we can calculate the potential energy:
PE = mgh
= (900 kg)(9.8 \(m/s^2\))(20 m)
= 176,400 J
Therefore, the potential energy of the roller coaster is 176,400 J (joules).
Know more about potential energy here:
https://brainly.com/question/21175118
#SPJ8
2x2 + 4 what is the sum
Answers
2x2 + 4 = 4 + 4 = 8
Therefore, the sum of 2x2 and 4 is 8.
What is the relationship between a substance’s thermal energy and its kinetic energy? There is no relationship between a substance’s thermal energy and kinetic energy.
There is no relationship between a substance’s thermal energy and kinetic energy.
As the substance’s thermal energy increases, the kinetic energy of its particles increases, and vice versa.
As the substance’s thermal energy increases, the kinetic energy of its particles increases, and vice versa.
As the substance’s thermal energy increases, the kinetic energy of its particles decreases, and vice versa.
As the substance’s thermal energy increases, the kinetic energy of its particles decreases, and vice versa.
A substance’s thermal energy is the same as its kinetic energy.
Answers
As the substance's thermal energy increases, the kinetic energy of its particles increases, and vice versa.
What is kinetic energy?The kinetic energy of an object increases as its mass or velocity increases. For example, a heavy object moving at a high speed has more kinetic energy than a lighter object moving at a lower speed. Additionally, the direction of an object's motion is not relevant to its kinetic energy, as long as it is moving. Kinetic energy is a scalar quantity, meaning that it has only magnitude and no direction. It is also a form of mechanical energy, which is energy that is associated with the motion or position of an object. Other forms of mechanical energy include potential energy, which is energy that an object possesses due to its position or configuration, and thermal energy, which is the energy associated with the motion of particles within a substance.
Here,
Thermal energy is a form of energy associated with the motion of particles in a substance. Specifically, thermal energy is the sum of the kinetic energies of the particles in a substance. So, as the temperature of a substance increases, the average kinetic energy of its particles also increases. This means that the particles move faster and have greater kinetic energy. Therefore, there is a direct relationship between a substance's thermal energy and its kinetic energy. If the substance's thermal energy increases, its particles will have more kinetic energy and will move faster. Conversely, if the substance's thermal energy decreases, its particles will have less kinetic energy and will move more slowly.
To know more about kinetic energy,
https://brainly.com/question/26472013
#SPJ1
Answers:
Question 1: As the substance’s thermal energy increases, the kinetic energy of its particles increases, and vice versa.
Question 2: Its molecules move around more quickly, so there is more space between them, making it less dense than the air above it.
Question 3: Warmer sauce at the bottom of the pot is less dense, so it rises, forcing cooler sauce down, where it is warmed.
Question 4: Hot soup warms the bowl where it sits.
Question 5: transfer of thermal energy through infrared waves
Explanation:
i just did the quick check
create a poem that incorporates those ten words. Feel free to make it as silly as you like! MINIMUM of 6 lines with a MINIMUM of 5 words and 10 should come from your book. These do not have to rhyme, but can if you wish.
Answers
I could make a poem for you if you actually gave the words...... what 10 words do i need to incorporate???☹︎
Calculate the altitude above the surface of Earth, in meters, at which the acceleration due to gravity is g
Answers
Answer:
By definition the acceleration due to gravity at the surface is g:
The altitude above the surface is zero for an acceleration of g.
A ball is projected at an angle of 53°. If the initial velocity is 48 meters/second, what is the vertical component of the velocity with which it was launched?
A.) 31 meters/second
B.) 38 meters/second
C.) 44 meters/second
D.) 55 meters/second
Answers
Answer:
The vertical component of the velocity can be found using the formula:
V₀y = V₀ * sin(θ)
where V₀ is the initial velocity, θ is the angle of projection, and V₀y is the vertical component of the velocity.
Substituting the given values, we have:
V₀y = 48 * sin(53°)
Using a calculator, we can evaluate sin(53°) to be approximately 0.799:
V₀y = 48 * 0.799
V₀y ≈ 38.352
Therefore, the vertical component of the velocity with which the ball was launched is approximately 38 meters/second, which corresponds to option B.
Answer:
B.) 38 meters/second
Explanation:

Two charged soap bubbles, bubble 1 and bubble 2, are deprecated by some distance r. Bubble 2 has 8 times the charge of bubble 1. Bubble 2 exerts a force of F1-2 on bubble 2, and bubble 2 exerts a force of F2-1 on bubble 2. How does the magnitude of F1-2 compare to F2-1?
A - It’s magnitude is 8 times as large
B - The two forces have the same magnitude
C - it’s magnitude is 64 times as large
D - it’s magnitude is 1/8 as large
Answers
Considering the information from bubble 1 and bubble 2, the magnitude of F1-2 compares to F2-1 because the two forces have the same magnitude. Option B is correct.
Why do the two forces have the same magnitude?This concept can be explained by physics through Coulomb's Law, which states that the electrostatic interaction between two particles occurs the greater the magnitude of the charges and the smaller the distance between the particles, the greater the force of attraction or repulsion between the charges.
Therefore, through Coulomb's Law we can understand the interaction between charged particles and the forces exerted by them that will be equal in magnitude and opposite in direction, making the magnitude of F1-2 equal to the force F2-1.
Find out more about Coulomb's Law on:
https://brainly.com/question/506926
#SPJ1
why is the unit of power called derived unit
Answers
Answer:The ampere is unique in that it uses the base unit of time (t) in its definition (second). All other electrical and magnetic units (such as voltage, power, and magnetic flux) use various combinations of base units in their definitions and are called derived units.
Explanation:
A 2.55 kg piece of lead at 40 degree Celsius is placed in a very large quantity of water at 10 degree Celsius and thermal equilibrium is eventually reached. Calculate the entropy change of the lead that occurs during this process. The specific heat of lead is 130 J/(kg K).
Answers
6.6 J/K
1.4 J/K
190 J/K
100 J/K
6.2 J/k
i think this is a answer
What mass of silver has a volume of 150 cm3?
Answers
ANSWER:
1573.5 g
STEP-BY-STEP EXPLANATION:
Given:
Volume (V) = 150 cm³
We have that the density of silver is 10.49 g/cm³, therefore, we calculate its mass, as follows:
\(\begin{gathered} d=\frac{m}{V} \\ \\ \text{ We replacing:} \\ \\ 10.49=\frac{m}{150} \\ \\ m=10.49\cdot150 \\ \\ m=1573.5\text{ g} \end{gathered}\)The mass of silver is 1573.5 grams
Chemical bonds are broken in which molecules? Question 1 options: C6H12O6 & H2O CO2 & O2 O2 & C6H12O6 CO2 & H2O
Answers
Answer:O2 & C6H12O6
Explanation:
C6H12O6 + 6O2-> 6CO2 + 6H2O
O2 and C6H12O6 molecules' chemical connections are disrupted.
What is chemical bond?A chemical bond, which is a powerful attraction between atoms, ions, or molecules, enables the construction of molecules. The connection could be brought on by electrostatic force.Overview of the fundamental types of... Bonds in chemical formula solid chemical ties. Covalent or ionic bonds are two different types of chemical bonding.A chemical bond is an attraction between two atoms or ions. To form bonds, atoms exchange or swap their valence electrons. Atoms need to form chemical bonds in order to attain a complete outer energy level, which is the most stable arrangement of electrons.A chemical bond is the binding force that binds various constituents (atoms, ions, etc.) in diverse chemical species.
C6H12O6 + 6O2-> 6CO2 + 6H2O
To learn more about chemical bond refer to :
https://brainly.com/question/819068
#SPJ2
Based on the diagram, what is the difference in how economic decisions are made in a mixed economy and a market economy? E.1.2
How Economic Decisions are Made
By the Government,
command
economy
By the Consumers
mixed
economy
market.
economy
O Consumers make all economic decisions in a mixed economy, while the government makes all economic decisions in a market economy.
Government and consumers make economic decisions in a mixed economy, while consumers make economic decisions in a market economy.
Government makes all economic decisions in a mixed economy, while consumers make all economic decisions in a market economy.
O Consumers make economic decisions in a mixed economy, while consumers and government make economic decisions in a market economy.
Answers
Based on the diagram, the correct statement is: Government and consumers make economic decisions in a mixed economy, while consumers make economic decisions in a market economy.
How do we explain?In a mixed economy, economic decisions are made by both the government and consumers.
The government plays a significant role in regulating and influencing economic activities through policies, regulations, and interventions.
In market economy, economic decisions are primarily made by consumers. The market forces of supply and demand dictate the allocation of resources, production levels, and pricing.
The freedom to buy and sell whatever they choose is what ultimately determines how commodities and services are produced and distributed.
Learn more about Economic Decisions at:
brainly.com/question/30296708
#SPJ1
